Recent Articles
Quickest Mobile Data Recovery Case: 100% of Data Recovered in One Hour
How to fix a corrupted database on PS4
How to Troubleshoot Black or Blank Screens in Windows
LockBit Ransomware: A Comprehensive Guide to the Most Prolific Cyber Threat
How To Use iPad Recovery Mode
How to Prevent Overwriting Files: Best Practices
External Hard Drive Not Showing Up On Windows – Solved
How to Fix a Corrupted iPhone Backup
Backup and Remote Wiping Procedures
Common VMware Issues and Troubleshooting Solutions

I think there's an issue with my storage device, but I'm not sure Start a free evaluation →
I need help getting my data back right now Call now (800) 972-3282
The reasons to delete a folder or file vary depending on the moment and the user. You may not need that file anymore, or the folder is occupying too much of your storage space. But while wiping the memory from junk and outdated information, you may encounter a challenge where you can’t delete the file or folder. To solve it, you might have to force deletion.
In this article, you check the reasons that are preventing you from deleting and how to fix the issue and release the space.
Why you can’t delete a file or folder
Most of the time, you can’t delete a file or folder because it’s in use. When a file or folder is opened or is a background process, Windows 10 locks it, hindering the user from modifying, relocating, or deleting it. On rare occasions, a virus attack may cause a file to become locked from deletion.
Here are common reasons for the “Can’t Delete File/Folder” problem:
The file or folder is in use
Opened files or folders prevent its deletion. However, this often occurs when the file is open in a background process as well.
System file restrictions
Windows may restrict the deletion of certain critical and essential files to prevent system instability.
File is corrupted or folder corruption
Corrupted files or folders can prevent their deletion using standard methods. To erase them from your computer you must follow specific steps.
Read-only status
Write protection may be enabled either manually or due to disk errors, preventing any type of modification.
Disk corruption
Like file and folder corruption, if the disk is corrupted, you will not be able to execute several actions, including deleting files.
Full recycle bin
When you delete files and folders, they are sent to the recycle bin from where you can restore them. If it reaches the capacity, you might not be able to delete more files. Also, some files and folders are too big for the recycle bin, meaning they must be permanently deleted.
Malware or virus infection
Malware or virus infections can interfere with file deletion processes by locking files, modifying system settings, or blocking access to critical functions.
How to force delete a file or folder in Windows 10 and 11
Before taking action to solve the issue of undeletable files, make sure that you have the following:
- Closed the file, folder, and applications via the Task Manager.
- Closed all programs.
- Scanned your machine with an antivirus to check the system for malicious programs and get rid of them, if any were found.
- Removed write protection on the device (if you can’t delete files from an SD card, USB pen, or external hard drive).
- Checked the file properties to ensure that the disk/file is not in a read-only state.
- Rebooted your computer.
Then try removing the obstinate file again. If the problem persists and you still can’t delete a file or folder, proceed to the next fix solutions.
Solution 1. Force deleting files/folders with CMD
If you can’t delete a file from your Windows 10 or 11 computer, you can try forced removal via Command Prompt (aka CMD).
You can also use these steps for wiping files from an external hard drive, SD card, USB stick, etc.
Using DEL command:
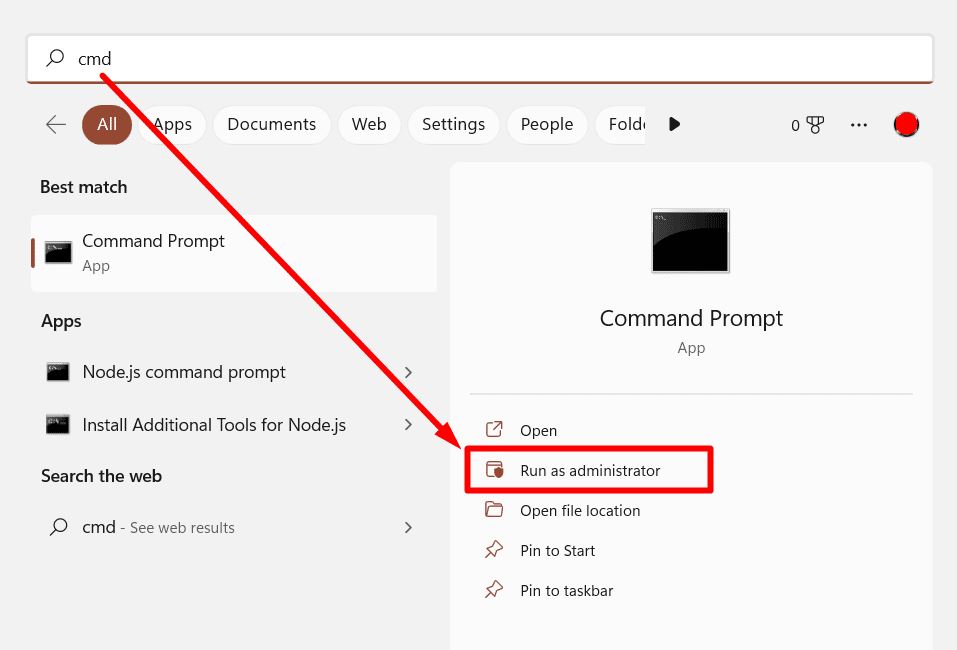
- Click the Start menu and type cmd
- Right-click the Command Prompt app and select Run as administrator from the menu list.
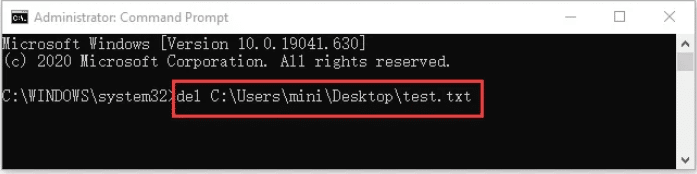
- Once in the Command Prompt window, type del file path, replacing the “file path” piece with the actual location of your target file.
Important: The file extension (.txt, .jpeg, .docx, .xls, whatever) must be included in the path.
In this example, the command del C:\Users\mini\Desktop\test.txt would delete the TXT file named “test” located on our desktop.
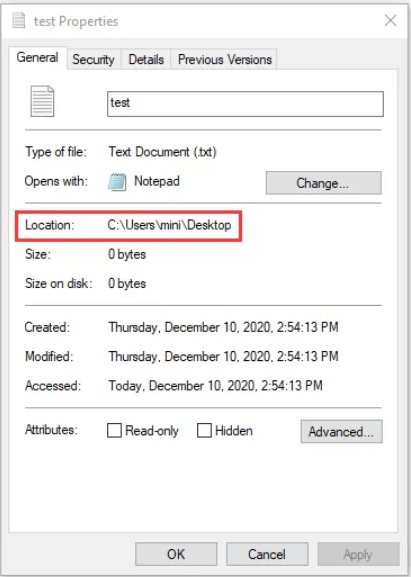
Pro tip: You can get the full path to a file or folder by simply right-clicking it and selecting Properties.
4. Hit Enter to execute the command.
Using RMDIR /S /Q command:
- Click the Start menu and type cmd
- Right-click the Command Prompt app and select Run as administrator from the menu list.
- Type rmdir /s /q folder path in the Command Prompt. Replace “file path” with the actual location of your target file.
- Press Enter to execute the command.
Solution 2. Run Windows 10 in Safe Mode to unlock and delete files
Rebooting the computer in Safe Mode helps fix issues by isolating the problem to something beyond the core system files and drivers, making troubleshooting easier. This method can be handy if you aren’t sure which process currently uses the file or if your computer was infected with a virus.
Here’s how to reboot into Safe Mode for both Windows 10 and 11:
- Press the Windows key + I to open Settings.
- Navigate to System > Recovery.
- Under “Advanced startup,” click Restart now.
- After your PC restarts, choose Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart.
- Select 4 or F4 for Safe Mode, or 5 or F5 for Safe Mode with Networking.

- Attempt to erase the file or folder while in Safe Mode.
- Restart your computer so it exits Safe Mode.
Solution 3. Use Shift + Delete to force remove file/folder
If a file won’t delete, selecting it and pressing the Shift + Delete keyboard shortcut is another way to erase the data permanently.
Also, in case the file has been corrupted or your Windows 10 machine reports that the file/folder can’t be found, you may need to perform a disk repair to see if it can work around the error and fix the corrupted system files.
Here’s how to do it using the CHKDSK command:
- Press the Windows + R key combination to launch Run Window.
- Next, type cmd in the window that opens, and hit OK.
- Once in the command prompt window, type in chkdsk # / f / r (replace # with the letter of the damaged drive).
- Hit Enter to execute the command.
Once the CHKDSK repair process is over, you can type Exit to close the command line window and go check if the “folder won’t delete” error has been fixed.
Solution 4: Try third-party software
There are innumerable third-party applications and tools for repairing corrupted data that can help you delete locked files.
Typically, these are lightweight programs with a user-friendly and intuitive interface that even the most inexperienced user can easily navigate. Make sure to read the reviews and check for data privacy certificates and policies before downloading and using third-party software.
Need deleted files back?
If some mix-up happened and you’ve accidentally deleted files and cleared the recycle bin, then it’s best to consult professionals. With great experience in data recovery from all kinds of drives and media storage, we at SalvageData would be happy to offer you a quick and accurate diagnosis of your device.
Providing top-notch data recovery services of any complexity for nearly two decades already, SalvageData remains trusted by numerous industry experts worldwide, which means you can count on us regardless of the drive model and the amount of data to be restored.











