I think there's an issue with my storage device, but I'm not sure Start a free evaluation →
I need help getting my data back right now Call now (800) 972-3282
Solid-state State Drives, or SSDs, have grown in popularity as a storage option for computers in recent years. Even though it’s a storage technology that costs more than HDD, their main competitor, SSD is reliable and faster, making them the first storage choice by many users. But, do you know how Solid-State Drives work?
How do Solid-State Drives work?
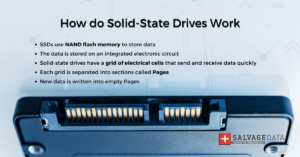
SSDs work by using flash memory to store data in onboard electrical cells.
Data is written to these cells by a controller, which works much like a USB port does for other storage devices. Whenever data is requested, the controller reads the data from the cells and sends it back to the requesting application.
SSDs work differently from traditional hard-disk drives. Inside SSDs, data is stored on an integrated circuit that consists of electronic circuits embedded within a silicon semiconductor cell. It’s a grid of electrical cells that send and receive data quickly.
Each grid is separated into sections called Pages. The data is stored on these pages.
Unlike HDDs, they don’t have any mechanical moving parts so they are more resistant to physical shock and vibration. They are also faster, smaller, lighter, and use less power than traditional hard-disk drives.
One more difference is that, while HDD writes new data on any location of its plate at any time, SSD can only write the new data on empty pages in the block. To hard drives, it means that the data can be overwritten. And to solid-state drives, it means that any data will never be overwritten.
The bad news is the more data, the less speed. Therefore, SSDs can slow their read/write speed over time.
How do SSDs store data
SSDs store data using a process called flash translation layer (FTL). This process allows the SSD to take multiple types of NAND chip technologies and treat them as one large block of storage space.
When data is written to an SSD, it is stored on the FTL in blocks. The FTL also keeps track of how much free space is available.
The process to save a new file on your SSD is:
The SSD will find a block with unused pages and then write on it in a block, marking the page.
To erase the data, the SSD also processes the block. Which means that all pages on the block are deleted. But, it’s not overwritten, making the process of data recovery for SSD easier than for other technologies.
What is SSD storage?
Solid-State Drives, known as SSD, is a storage device that uses a non-volatile form of flash memory to store and access data.
Unlike traditional hard-disk drives, they don’t use mechanical moving parts. This makes them faster, smaller, and lighter. Also, SSDs are not prone to easily fail, even though they have a shorter lifespan compared to HDDs.
Solid-state drives store your data in flash memory and not a magnetic system like HDD. The data is retained in a cluster of memory banks. Since this is a non-volatile memory, power loss does not cause data loss.

What are solid-state drives used for?
You can see SSDs in most devices that require data storage and high read/write speeds.
Gaming: Computers and laptops optimized for gaming have to offer cut-edge technology. Each day, games have more quality graphics, occupying more storage space and demanding better and faster technology. To boost gaming performance, gamers and enthusiasts are always looking for devices that can follow their game-of-the-year requirements. And SSDs are the storage technology delivering it. PCs, PlayStation, Xbox, and many other devices, have the solid-state drive for better performance.
Working: Several companies and professionals rely on their SSDs to create their portfolios. With heavy software, some photographers, video editors, content creators, architects, and more professionals, solid-state drives are the best-fit solution for performance.
Studying: SSDs are also shock resistant. This is great for students and users that have their laptops always on their backpacks. Their resistance makes solid-state drives a reliable choice for everyday devices since it reduces the chances of data loss when mobile devices are dropped.
SSD vs HDD: What’s the difference?

These two storage technologies have their advantages that, once combined, can generate a near-perfect data storage solution while we wait for future improved storage technologies. You can, for example, use both of them on your computer or laptop to increase speed (SSD) and have large storage (HDD). Businesses can also benefit from this combination by using RAID with SSD and HDD.
Our experts have compiled a detailed article detailing the pros and cons of each of these storage technologies. The main differences to consider when comparing SSDs vs. HDDs are how they store data and their price per gigabyte (GB).
TL; DR: SSDs are storage devices that use a non-volatile form of flash memory to store and access data. They don’t have any mechanical moving parts. Which makes them faster, smaller, lighter, and more resistant to physical shock and vibration than traditional hard-disk drives. SSDs write data to integrated circuits using a process called flash translation layer (FTL). This allows for multiple types of NAND chip technologies to be treated as one large block of storage space.